GRAM-POSITIVE BACTERIA
|
GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA
| COCCI | RODS ACID FAST
BACTERIA | COCCI SPIROCHETES SPIRILLI | RODS |
|
|
GRAM-POSITIVE BACTERIA |
GRAM-POSITIVE COCCI | |
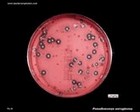
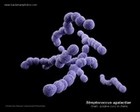
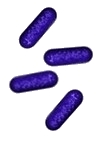
 | | Staphylococcus | 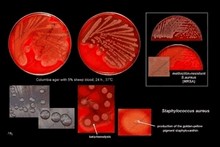 | | Gram stain: | Gram-positive | | Microscopic appearance: | cocci in grape-like clusters | | Oxygen relationship: | facultatively anaerobic bacteria |
| Motility: | nonmotile | | Catalase test: | catalase-positive | | Oxidase test: | negative* | | Spores: | non-spore forming | | | * Some species (non-human isolates) are positive |
|
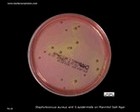
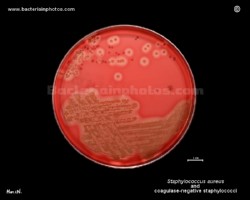
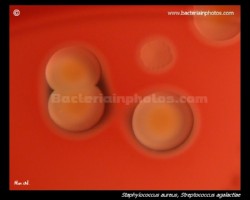
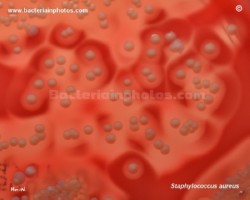
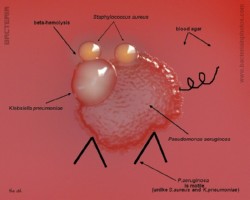
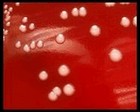
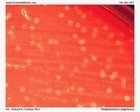
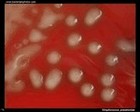
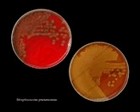
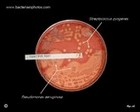
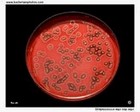
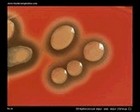
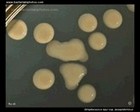
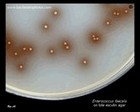
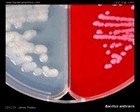
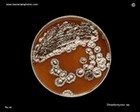
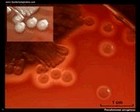
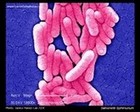
Staphylococcus aureus | - Beta-hemolysis on media with blood (sheep, horse)
- Yellow-pigmented colonies
- NaCl tolerant (7.5%), mannitol fermentation
- Production of coagulase (free and cell-bound coagulase)
- Lithium chloride and potassium tellurite tolerant
- Lecithinase production and lipase activity
| |
|
 |
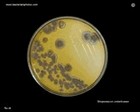
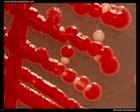
| Beta-hemolysis on media with blood |
|
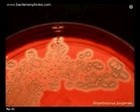
 Beta hemolysis
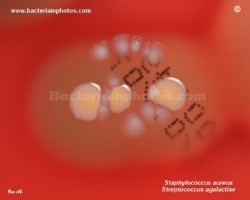
Staphylococcus aureus |
 Staphylococcus aureus
Beta hemolysis on blood agar |
 Staphylococcus aureus
Beta hemolysis on blood agar |
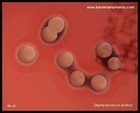 Staphylococcus aureus
Colonies on blood agar |
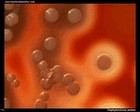 Staphylococcus aureus
Beta hemolysis,
weak pigmentation |
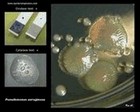
Colonies of Staphylococcus aureus are usually yellow-pigmented and beta-hemolytic
(but not always!) |
 Staphylococcus aureus
non-pigmented colonies
weak hemolysis |
 Staph. aureus
non-pigmented strain |
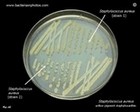 S.aureus
two shades of yellow... |
 Staphylococcus aureus
staphyloxanthin |
| Yellow colonies (staphyloxanthin) |
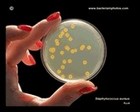 Staphylococcus aureus
yellow colonies on TSA |
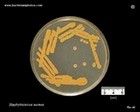 Staphylococcus aureus
on Brain Heart Infusion Agar |
 Staphylococcus aureus
on Tryptic Soy Agar |
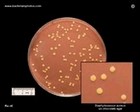 Staphylococcus aureus
Chocolate Agar |
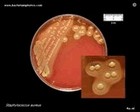 Staphylococcus aureus
on Schaedler Agar |
 Staphylococcus aureus
Beta-hemolytic colonies |
 Staphylococcus aureus
on Tryptic Soy Agar |
 Staphylococcus aureus and
Staphylococcus epidermidis
on Chocolate Agar
|  Catalase test
|
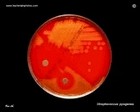
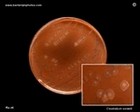
 Staphylococcus aureus
on Baird Parker Agar |
 Staphylococcus aureus
and S.epidermidis
Baird Parker Agar |
 Colonies of S.aureus
lecithinase +, lipase + |
 Staphylococcus aureus
and S.epidermidis
Mannitol Salt Agar |
 Staphylococcus aureus
Mannitol Salt Agar
Mannitol + |
Methicilin Resistant S.aureus
MRSA | |
 MRSA Staphylococcus aureus
on Brilliance MRSA
Chromogenic Agar |
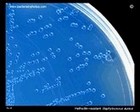 Staphylococcus aureus
ORSAB |
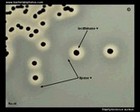
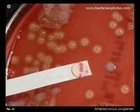
 The disc diffusion testing |
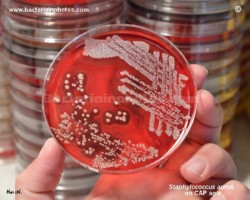
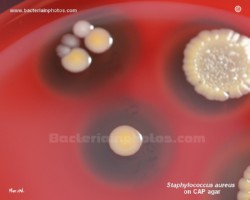
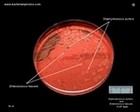 S.aureus and E.faecalis
on CAP agar |
 S.aureus colony |
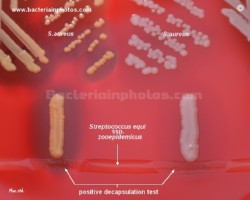
Clumping factor
(Bound coagulase) | Decapsulation
test | Biofilm
formation | Susceptibility to
antibiotics | S.aureus
and penicillin (it saved millions...)
80,000,000??
200,000,000?? |
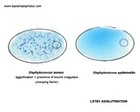 Bound coagulase
(clumping factor) |
 Hyaluronidase |
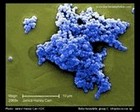
 Staphylococcus aureus
biofilm formation |
 The disc diffusion testing |
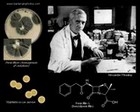 Staphylococcus aureus
and discovery of penicillin |
| Images of Staphylococcus aureus |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
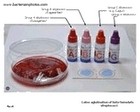
Antibiotic Treatment
Should be always guided by in vitro susceptibility tests!
Selection of appropriate antibiotics depends on diagnosis! | | IF SUSCEPTIBLE: Treatment of Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) | | Penicillins | Cephalosporins | Lincosamides | Alternatives | | | | | Treatment of Methicillin-Rresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) | | Glycopeptides |
Sulfonamides | Lipopeptides | Oxazolidonones | | | | |
| Tetracyclines | Lincosamides | Streptogramins | Rifamycins | | | | |  | Useful links |
|
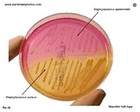
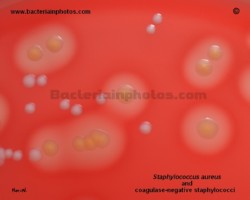
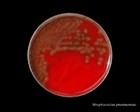
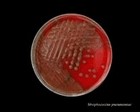
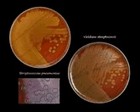
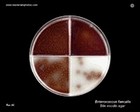
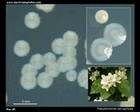
Staphylococcus epidermidis | - Gamma-hemolysis on media with blood (sheep, horse)
- White colonies
- NaCl tolerant (7.5%), doesn't ferment mannitol
- Coagulase negative
- Lecithinase, lipase negative
| |
|
 Staphylococcus epidermidis
on Tryptic Soy Agar
|
 Staphylococcus epidermidis
|
 Staphylococcus epidermidis on
blood agar |
 Staphylococcus epidermidis
colonies on blood agar |
 Staphylococcus epidermidis
on CAP agar |
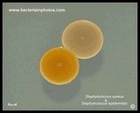 Staphylococcus epidermidis
and Staphylococcus aureus
|
 S.epidermidis, S.aureus,
E.faecalis on Tryptic Soy
Agar |
 Staphylococcus epidermidis
on Tryptic Soy Agar
|
| |
|
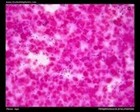
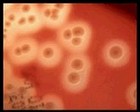
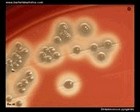
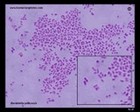
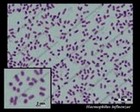
Staphylococcus sp. micrographs |
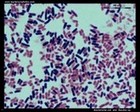
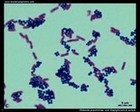 Staphylococcus aureus
and Klebsiella pneumoniae
(Gram stain) |
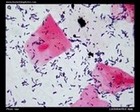
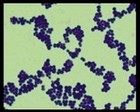 Staphylococcus aureus micrograph
(Gram stain) |
 Staphylococcus aureus
Gram stain |
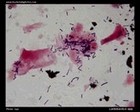
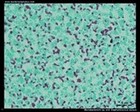 Staphylococcus aureus
Ziehl-Neelsen stain |
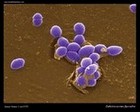
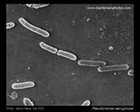
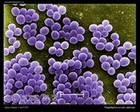 Staphylococcus aureus
SEM micrograph |
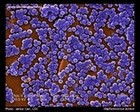 Staphylococcus aureus
SEM |
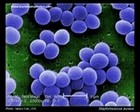 Staphylococcus aureus
SEM micrograph |
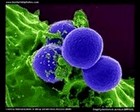 Staphylococcus aureus
MRSA |
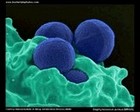 MRSA micrograph
methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus |
 |
| Three-dimensional (3D) computer-generated images |
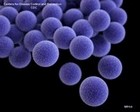 Image of MRSA
|
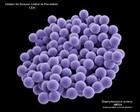 Staphylococcus
MRSA |
 Vancomycin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus |
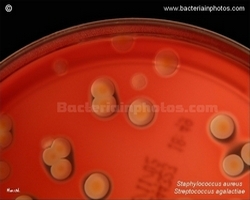
 | | Streptococcus | | | Gram stain: | Gram-positive | | Microscopic appearance: | cocci in chains (liquid media)
or pairs | |
Oxygen relationship: | facultatively anaerobic bacteria | | Motility: | nonmotile | | Catalase test: | catalase-negative | | Oxidase test: | negative | | Spores: | non-spore forming | | | |
|
ALPHA-HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI
VIRIDANS STREPTOCOCCI
- Mitis Group: e.g. S.mitis, S.oralis, S.sanguis (part of the normal dental plaque flora)
- Anginosus Group: e.g.S.anginosus, S.constellatus, S.intermedius (oral, genitourinary flora, gastrointestinal tract); can be beta-hemolytic
- Mutans Group: e.g.S.mutans (associated with dental caries); some strains can be beta-hemolytic
- Salivarius Group: e.g.S.salivarius, S.vestibularis (oral cavity)
- Bovis Group: e.g.S.bovis
- Clinical significance: some of them can be the causative agents of subacute endocarditis, abscesses and infections in neutropenic patients
| |

Alpha and gamma
hemolysis |

Alpha-hemolytic streptococci
throat swab |
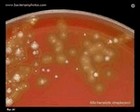 Viridans streptococci |

Viridans streptococci |

Streptococcus spp.
viridans streptococci
optochin resistant |
 Streptococcus anginosus
on BAP |
 Streptococcus mitis
blood culture |
 Streptococcus mutans |
 Viridans streptococci
blood culture specimen |
Antibiotic Treatment
Should be always guided by in vitro susceptibility tests!
Selection of appropriate antibiotics depends on diagnosis! | | Endocarditis |
| Penicillins | Cephalosporins | Glycopeptides | Alternatives | |
|
| | | |
|
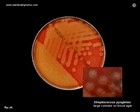
PNEUMOCOCCUS
- Oropharyngeal carriage of pneumococci is common
- An important agent of community-acquired pneumonia
- Otitis media, sinusitis, meningitis, endocarditis
- Require elevated CO2 concentrations (incubation in an atmosphere containing 5% - 10% CO2)
- Sensitive to optochin
- Soluble in bile salts
- Positive Quellung test
|
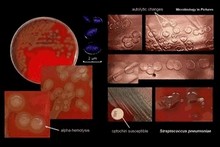 |
|

Streptococcus pneumoniae
on blood agar |
 Streptococcus pneumoniae
depressed centers of colonies |
 Streptococcus pneumoniae
virulent strain |

Streptococcus pneumoniae
alpha-hemolysis
under colonies |
 Streptococcus pneumoniae
avirulent strain |

Streptococcus pneumoniae
optochin test
Comparision of virulent
and avirulent strain |

Streptococcus pneumoniae
bile solubility test |

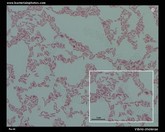
Streptococcus pneumoniae
in sputum (micrograph) |
 Streptococcus pneumoniae
in cerebral spinal fluid |  |
 Streptococcus pneumoniae
on Petri dish
virulent strain |
 Streptococcus pneumoniae
on blood agar
virulent strain |
 Streptococcus pneumoniae
virulent and
avirulent strain |
 Streptococcus pneumoniae
avirulent strain and
viridans streptococci |
 Streptococcus pneumoniae
3D model |
|
Antibiotic Treatment
Should be always guided by in vitro susceptibility tests!
Selection of appropriate antibiotics depends on diagnosis! | | Penicillin sensitive Streptococcus pneumoniae | | Penicillins | Cephalosporins | Macrolides | Alternatives | | | | | | Penicillin resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae | | Cephalosporins | Glycopeptides | Alternatives | | |
| | |
|
|
- Group A Lancefield antigen
- PYRase positive
- bacitracin susceptible
|

|
 Beta and gamma
hemolysis
(GAS = Group A Strep.) |
.jpg) Beta and gamma
hemolysis |
 Streptococcus pyogenes
on blood agar
large colonies |
 Streptococcus pyogenes
PYRase positive |
 Beta hemolysis
on sheep blood agar
(S.pyogenes) |
 Streptococcus pyogenes
beta hemolysis |
 Colonies of
Streptococcus pyogenes |
 Colonies of S.pyogenes
on blood agar |
 Beta hemolysis
Beta-hemolytic colonies of
S.pyogenes |
 PYRase
(PYR test) |
 Sensitive to penicillin
|
 Latex agglutination
|
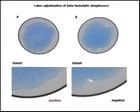 Group A Streptococcus
latex agglutination |
 Streptococcus pyogenes
3D
computer-generated image |
 Strep throat |
|
|
Antibiotic Treatment
Should be always guided by in vitro susceptibility tests!
Selection of appropriate antibiotics depends on diagnosis! | | | | Penicillins | Cephalosporins | Macrolides
(patients allergic to penicillin) | Alternatives | |
- Peroral cephalosporins (I, II)
| | | |
| |
|
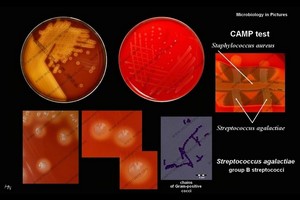
- Group B Lancefield antigen
- CAMP test positive
- hydrolyze sodium hippurate
- Often weaker (partial) beta-hemolysis
|
 |
 |
 Streptococcus agalactiae
|

Streptococcus agalactiae
|
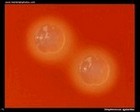 Streptococcus agalactiae
on blood agar |
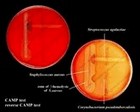 Positive CAMP test |
 CAMP test and
reverse CAMP test |
 CAMP test
detail |
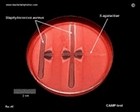 CAMP test
on Petri dish |
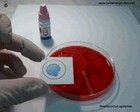 Latex agglutination
of GBS
|  Biochemical identification of
S.agalactiae |
 Streptococcus agalactiae
3D model |
|
Antibiotic Treatment
Should be always guided by in vitro susceptibility tests!
Selection of appropriate antibiotics depends on diagnosis! | | | | Penicillins | Cephalosporins | Macrolides
(patients allergic to penicillin) | Alternatives | |
- Peroral cephalosporins (I, II)
| | | | | |
BETA-HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI OF GROUP C |
 Streptococcus equi ssp. equi
on Petri dish |
 Streptococcus equi ssp. equi
colonies on blood agar |
 Streptococcus zooepidemicus
on blood agar |
 Streptococcus equi ssp.
equi on blood agar
|  Streptococcus
zooepidemicus on
tryptic soy agar |
 Streptococcus
zooepidemicus on brain heart agar |
Streptococcus sp. micrographs |
 Streptococcus agalactiae
micrograph |
 Streptococcus sp.
|
 Streptococcus pyogenes
Gram stain |
 Streptococcus sp.
Group C
|
 Streptococcus sp.
|
BETA-HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI OF GROUP F and G |
| |
|
| |
 | | Enterococcus |
 | | Gram stain: | Gram-positive | | Microscopic appearance: | cocci or ovoid cocci in pairs, clusters or short chains (liquid media) | | Oxygen relationship: | facultatively anaerobic bacteria | | Motility: | nonmotile or motile | | Catalase test: | catalase-negative
| | Oxidase test: |
negative | | Spores: | non-spore forming | | | |
|
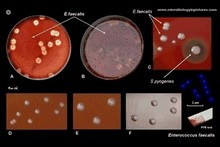
 Enterococcus faecalis |  Enterococcus faecalis | 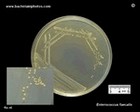 Enterococcus faecalis | 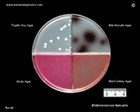 Enterococcus faecalis |
 Enterococcus
|
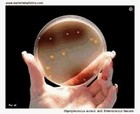 Enterococcus faecalis |  Enterococcus faecium
|  Enterococcus faecalis | 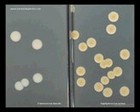 Enterococcus faecalis and Staphylococcus aureus
| 
Enterococcus faecalis
|
 Enterococcus faecalis |
 Enterococcus faecalis |
 Enterococcus faecalis
on blood agar |
 Enterococcus faecium
|
 Enterococcus
|
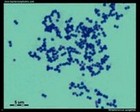
 Enterococcus faecalis
Gram stain |
 Enterococcus faecalis
scanning electron micrograph
(SEM) |
| Useful links |
GRAM-POSITIVE BACILLI (RODS) | |
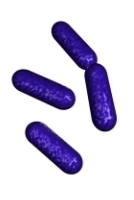 | | Listeria | 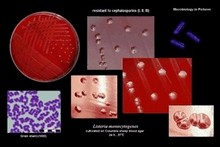 | | Gram stain: | Gram-positive | | Microscopic appearance: | short rods (sometimes coccoid forms), single or in chains | | Oxygen relationship: |
facultatively anaerobic bacteria | | Motility: | motile (at 20-25°C)*; peritrichous flagella | | Catalase test: | catalase-positive | | Oxidase test: | negative | | Spores: | non-spore forming | | | * optimal growth temperature at 30-37°C | | Listeria monocytogenes is the causative agent of listeriosis |
|
 |
 Listeria monocytogenes
on blood agar |
 Listeria monocytogenes
on blood agar |
 Listeria monocytogenes
on blood agar |
 Listeria monocytogenes
on blood agar |
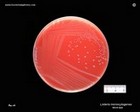 Listeria monocytogenes
|
 Listeria monocytogenes
beta hemolysis |
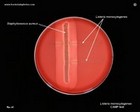 Listeria monocytogenes
CAMP test |
 Listeria monocytogenes
colonies on blood agar |
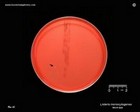 Listeria monocytogenes
on blood agar |
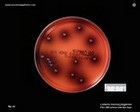 Listeria monocytogenes
PALCAM agar |
 Listeria monocytogenes
ampicillin susceptibility |
 Listeria monocytogenes
susceptibility to antibiotics |
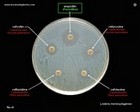 Listeria monocytogenes
susceptibility to
cephalosporins |
 Listeria monocytogenes
Gram-stain |
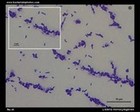 Listeria monocytogenes
microscopy |
 Listeria monocytogenes |
| Useful links |
| Useful links |
 | |
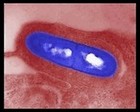
Corynebacterium | 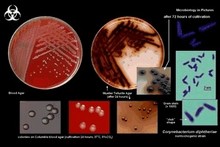 | | Gram stain: | Gram-positive | | Microscopic appearance: | rods, often broader at one end
("club" shape), grouped together
in a characteristic way ("V", "palisades", "Chinese letters") | | Oxygen relationship: | facultatively anaerobic bacteria | |
Motility: | nonmotile | | Catalase test: | catalase-positive | | Oxidase test: | negative | | Spores: | non-spore forming* | | | *metachromatic granules are often present. | | Corynebacterium diphtheriae is the causative agent of diphtheria |
|
 |
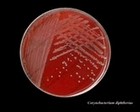 Corynebacterium diphtheriae
|
 Corynebacterium diphtheriae
|
 Corynebacterium diphtheriae
|
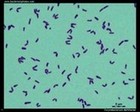 Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Gram stain |
 C.pseudotuberculosis
on blood agar |
| Useful links |
 | |
Bacillus | | | Gram stain: | Gram-positive | | Microscopic appearance: | rods in chains | | Oxygen relationship: | aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacteria | | Motility: | motile (peritrichous flagella) or nonmotile (e.g., B.anthracis) | | Catalase test: | catalase-positive | | Oxidase test: |
negative | | Spores: | spore forming (endospores) | | | | | Bacillus anthracis is the causative agent of anthrax |
|
 |
 Bacillus cereus |
 Bacillus cereus
on blood agar |
 Bacillus subtilis |
 Bacillus subtilis |
 Bacillus subtilis |
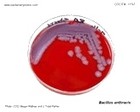 Bacillus anthracis
causative agent of anthrax |
 Bacillus anthracis
|
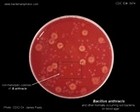 Bacillus anthracis
on blood agar |
 Bacillus anthracis
colonies on blood agar |
 Bacillus anthracis
capsule production |
 Bacillus anthracis
|
 Bacillus sp.
colonies on Mueller-Hinton agar |

Bacillus mycoides
|
 Bacillus mycoides
growth on agar |
 Serratia marcescens
and Bacillus mycoides |
 Bacillus mycoides
Gram stain |
 Gram-positive
sporulating bacterium
|
 Bacillus anthracis
micrograph
|
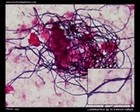
 Escherichia coli
and
Bacillus sp.
Gram stain |
| Useful links
|
|
 | | Lactobacillus | | | Gram stain: | Gram-positive | | Microscopic appearance: | rods in chains or palisades | | Oxygen relationship: | facultatively anaerobic or anaerobic bacteria | | Motility: | nonmotile (most of them) |
| Catalase test: | negative | | Oxidase test: | negative | | Spores: | non-spore forming | | | |
|
|
|
|

| |
| Useful links |
 | | Streptomyces | 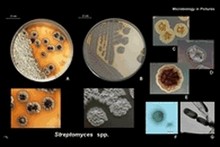 | | Gram stain: | Gram-positive | | Microscopic appearance: | rods; form substrate and aerial mycelium | | Oxygen relationship: |
aerobic bacteria | | Motility: | nonmotile | | Catalase test: | positive | | Oxidase test: | negative | | Spores: | spore forming (aerial mycelium) | | | |
|
 Streptomyces spp. |

Streptomyces spp.
|
 Streptomyces coelicolor
on Mueller-Hinton agar |
.jpg) Streptomyces coelicolor
colony on Mueller-Hinton agar |
 Streptomyces sp.
on agar plate |
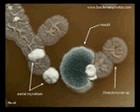 Streptomyces sp. |
 Streptomyces sp. |
 Streptomyces sp. |
 Streptomyces sp. |
 Streptomyces sp. |
| Useful links |
 | | Clostridium | | | Gram stain: | Gram-positive (young cultures), often Gram-variable | | Microscopic appearance: | rods (in pairs or chains) | | Oxygen relationship: | anaerobic bacteria | | Motility: | usually motile
(peritrichous flagella) | | Catalase test: |
negative | | Oxidase test: | negative | | Spores: | spore forming (endospores) | | | |
|
 |
 Clostridium sordellii |
 Clostridium sordellii
colonies |
 Clostridium perfringens |
 Clostridium perfringens |
 Clostridium perfringens |
 Clostridium sordellii
micrograph |
 Clostridium ramosum |
| Useful links |
|
GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA |
GRAM-NEGATIVE COCCI | |
 | | Neisseria | 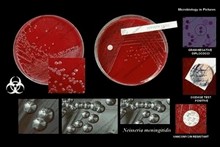 | | Gram stain: | Gram-negative | | Microscopic appearance: |
diplococci, cocci | | Oxygen relationship: | aerobic bacteria | | Motility: | nonmotile
| | Catalase test: | positive | | Oxidase test: | positive | | Spores: | non-spore forming | | | |
|
Neisseria meningitidis - growth on blood agar
- CO2 enhances growth, but is not required
- acid production from glucose and maltose
| | Neisseria gonorrhoeae - fastidious in its growth requirements
- special media for cultivation
- most strains require an atmosphere containing CO2
- colonies are well developed after 48 hr.
- four colony types have been recognized (T1-T4)
- acid production from glucose (maltose negat.)
|
 Colonies of
Neisseria meningitidis |
 Neisseria meningitidis
on blood agar | |
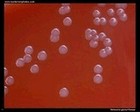 Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
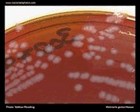 Neisseria gonorrhoeae
on New York City Agar |
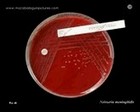 Colonies of
Neisseria meningitidis
Oxidase test + |

Neisseria meningitidis
Biochemical identification | |
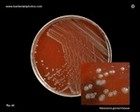 Neisseria gonorrhoeae
|
 Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
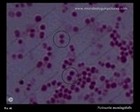 Neisseria meningitidis
micrograph |

Neisseria meningitidis
Oxidase test | |
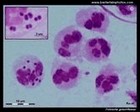 Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
 | | Moraxella (Branhamella) | 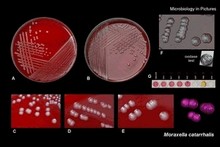 | | Gram stain: | Gram-negative |
| Microscopic appearance: | diplococci, cocci, cocobacilli | | Oxygen relationship: | aerobic bacteria* | | Motility: | nonmotile
| | Catalase test: | positive | | Oxidase test: | positive | | Spores: | non-spore forming | | | * some facultatively anaerobic |
|

Moraxella catarrhalis
|
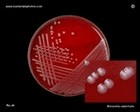 Moraxella catarrhalis
on blood agar |
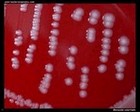 Moraxella catarrhalis
on blood agar |
 Moraxella catarrhalis
|
 Moraxella catarrhalis
Gram stain |
| Useful links |
 | | Bordetella | 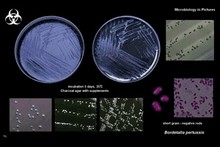 | | Gram stain: | Gram-negative | | Microscopic appearance: | small rods or cocobacilli | | Oxygen relationship: | aerobic bacteria |
| Motility: | nonmotile or motile
| | Catalase test: | positive | | Oxidase test: | positive | | Spores: | non-spore forming | | | |
|
 |
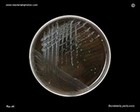 Bordetella pertussis
on charcoal agar |
 Bordetella pertussis
on charcoal agar |
 Bordetella pertussis
|
 | | Haemophilus |
 | | Gram stain: | Gram-negative | | Microscopic appearance: | small pleomorphic rods | | Oxygen relationship: | facultatively anaerobic bacteria | | Motility: | nonmotile
| | Catalase test: | variable | | Oxidase test: | variable | |
Spores: | non-spore forming | | | |
|
 |
 Haemophilus influenzae
on chocolate agar |
 Haemophilus influenzae
on chocolate agar |
 Haemophilus influenzae
on chocolate agar |
 Haemophilus influenzae
on blood agar
Satellite test |
 Haemophilus influenzae
Satellite test |
 Haemophilus influenzae
X + V factor |
 Haemophilus influenzae
micrograph
Pleomorphic G- bacilli |
 | |
Pseudomonas | | | Gram stain: | Gram-negative | | Microscopic appearance: | rods | | Oxygen relationship: | aerobic bacteria | | Motility: | motile (rarely nonmotile)
| | Catalase test: | positive | | Oxidase test: | positive or negative | | Spores: |
non-spore forming | | | |
|
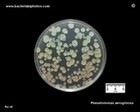
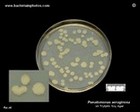 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
on Tryptic Soy Agar |
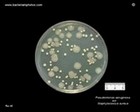
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
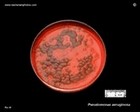
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
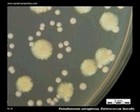
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
on blood agar |
 Colony of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
and Staphylococcus aureus |
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa and
Enterococcus faecalis |
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
on Tryptic Soy Agar |
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
on Tryptic Soy Agar |
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa,
Staphylococcus aureus,
Enterococcus faecalis |
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
and Staphylococcus aureus
on TSA |
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
colonies on blood agar |
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
on cetrimide agar |

Pseudomonas sp. |
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
 Staphylococcus spp.
and P.aeruginosa on blood agar |
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
 | |
Enterobacteriaceae | 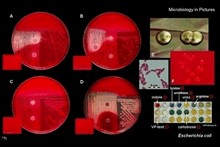 | | Gram stain: | Gram-negative | | Microscopic appearance: | rods | | Oxygen relationship: | facultatively anaerobic bacteria | | Motility: | motile (peritrichous flagella) or nonmotile | | Catalase test: |
positive | | Oxidase test: | negative (with exception of Plesiomonas spp.) | | Spores: | non-spore forming |
|
Escherichia coli |
 |
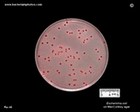 Escherichia coli
on MacConkey agar |
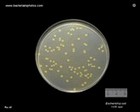 Escherichia coli
on CLED agar |
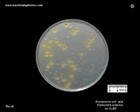 Escherichia coli
on CLED agar |
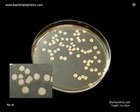 Escherichia coli
on Brain Heart Infusion Agar |
 Escherichia coli
on Tryptic Soy Agar |
 Escherichia coli
on MacConkey agar |
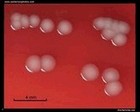 Escherichia coli
on blood agar |
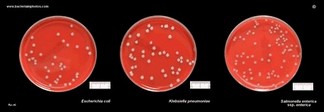 Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Salmonella enterica
on blood agar |
 Escherichia coli
on MacConkey agar |
 Escherichia coli
on Endo agar |
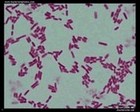 Escherichia coli
Gram stain |
 Escherichia coli
scanning electron micrograph
(SEM) |
 Escherichia coli
identification |
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
 Klebsiella pneumoniae
|

Klebsiella pneumoniae
on MacConkey |
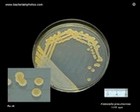 Klebsiella pneumoniae
on CLED |
 Klebsiella pneumoniae
on Endo |
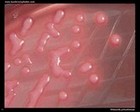 Klebsiella pneumoniae
on MacConkey agar |
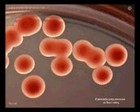 K.pneumoniae colonies
on MacConkey
|
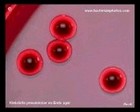 Klebsiella pneumoniae
on Endo agar |
 Klebsiella pneumoniae
on desoxycholate-citrate agar |
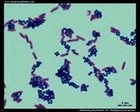 Klebsiella pneumoniae
and
Staphylococcus aureus
Gram stain |
 Klebsiella pneumoniae
identification |
Salmonella enterica |
 |
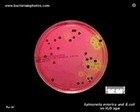 Salmonella and E.coli
on XLD | 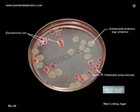 Salmonella, E.coli, Klebsiella
on MacConkey |  Salmonella
|  Salmonella
on XLD |
 Salmonella enterica
on Deoxycholate Citrate Agar |
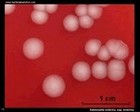 Salmonella enterica
on blood agar |
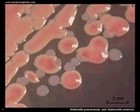 Salmonella enterica and
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
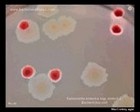 Salmonella and
E.coli on MacConkey |
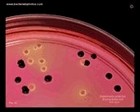 Salmonella enterica
and E.coli on XLD |
 Salmonella enterica
on MacConkey |
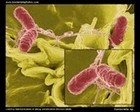 Salmonella enterica
SEM |
 Salmonella enterica
SEM |
 Salmonella
identification |
Serratia marcescens |

Serratia marcescens
CLED |
 Serratia marcescens prodigiosin |
 Serratia marcescens
|
 Serratia marcescens
MacConkey |
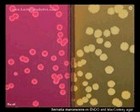 Serratia marcescens
on ENDO and MacConkey |
Citrobacter | Enterobacter |
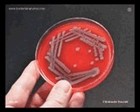 Citrobacter freundii
blood agar |
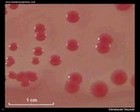 Citrobacter freundii |
 Enterobacter sakazakii
on Endo agar |
 Enterobacter cloacae
Gram stain |
Proteus |
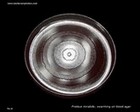 Proteus mirabilis
blood agar |
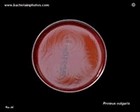 Proteus vulgaris
blood agar |
 Proteus mirabilis
Tryptic Soy Agar |
 Proteus mirabilis
blood agar |
 Proteus mirabilis
CLED |
 Proteus vulgaris
identification |
 Providencia rettgeri
on Endo agar |
 Morganella morganii
on blood agar |
 | | Yersinia | 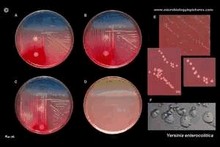 | | Gram stain: | Gram-negative | | Microscopic appearance: | rods or cocobacilli | | Oxygen relationship: | facultatively anaerobic bacteria | | Motility: |
motile or nonmotile at 30°C
nonmotile at 37°C
| | Catalase test: | positive | | Oxidase test: | negative | | Spores: | non-spore forming | | | | | Yersinia pestis is the causative agent of plague |
|
 |
 Yersinia pestis on blood agar
|
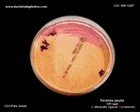 Yersinia pestis on CIN agar
|
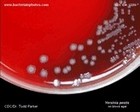 Yersinia pestis
colonies on blood agar
|

Yersinia pestis
colonies on blood agar
|
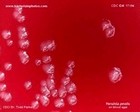 Yersinia pestis
colonies on blood agar |
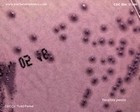 Yersinia pestis
CIN agar |
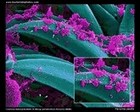 Yersinia pestis
SEM |
 Yersinia pestis
|
 Plague cycles
in the USA |
 Distribution of plague
in the USA |
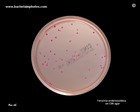 Yersinia enterocolitica
on CIN agar |
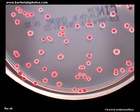 Yersinia enterocolitica
colonies on CIN agar |
 Yersinia enterocolitica
colonies on MacConkey agar |
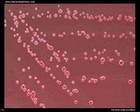 Yersinia enterocolitica
on Endo agar |
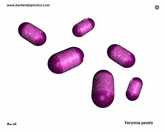 Yersinia pestis
|
 Yersinia enterocolitica
biochemical identification |
 | |
Vibrio | | | Gram stain: | Gram-negative | | Microscopic appearance: | curved rods (vibrios) or straight rods | | Oxygen relationship: | facultatively anaerobic bacteria | | Motility: | motile | | Catalase test: |
positive | | Oxidase test: | positive | | Spores: | non-spore forming |
|
 |
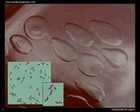
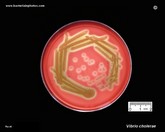 Vibrio cholerae
beta-hemolytic strain |
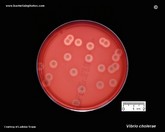 Vibrio cholerae
colonies on blood agar
|
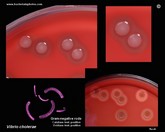 Vibrio cholerae
colony morphology |
 Vibrio cholerae
colonies |
 Vibrio cholerae
positive oxidase test
|
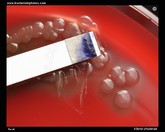
 String test with
Vibrio cholerae |
 Vibrio cholerae
growth in a liquid medium
|
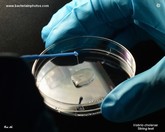
 Vibrio cholerae
on MacConkey agar
|
 Vibrio cholerae
Polymyxin B |
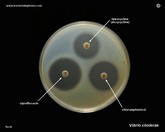 Vibrio cholerae
susceptibility testing
|
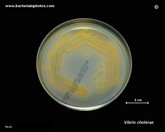 Vibrio cholerae
on TCBS agar |
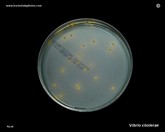 Vibrio cholerae
colonies on TCBS agar |
 Vibrio cholerae
on TCBS |
 Vibrio parahaemolyticus
on TCBS agar |
 Vibrio parahaemolyticus
on TCBS agar |
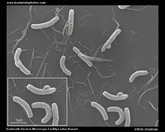 Vibrio cholerae |
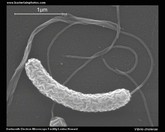 Vibrio cholerae
micrograph
(SEM) |
 Vibrio cholerae |
 Vibrio cholerae
Gram-stain |
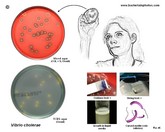 Tests for identification |
| |
Campylobacter | | | Gram stain: | Gram-negative | | Microscopic appearance: | spirilli, sometimes coccoid bodies | | Oxygen relationship: | microaerobic (O2 concentration 3 - 15%,
CO2 3 - 5%)
some can grow aerobically or anaerobically | | Motility: | motile
| | Catalase test: | positive | | Oxidase test: |
positive | | Spores: | non-spore forming | | | |
|
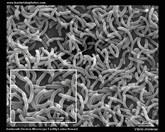
 Campylobacter jejuni |
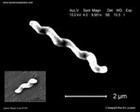 Campylobacter jejuni
scanning electron micrograph
(SEM) |
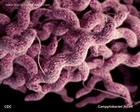 Campylobacter jejuni
scanning electron micrograph
(SEM) |
 | | Borrelia | | | Gram stain: | Not classified as either Gram-positive or Gram-negative
(the cells stain a weak Gram-negative) | | Microscopic appearance: |
Spirochetes | | Oxygen relationship: | microaerobic | | Motility: | motile
| | Catalase test: | - | | Oxidase test: | - | | Spores: | non-spore forming | | | |
|
| Borrelia burgdorferi is the causative agent of Lyme disease |
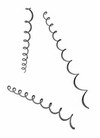
 Borrelia burgdorferi
scanning electron micrograph
SEM |
 Borrelia burgdorferi
SEM |
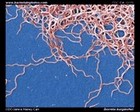 Borrelia burgdorferi
SEM |
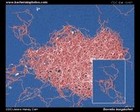 Borrelia burgdorferi:
Lyme disease
|
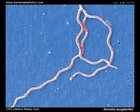
 Borrelia burgdorferi:
darkfield microscopy
|
 Ticks as vectors for
Borrelia burgdorferi |

Erythema migrans |
ACID-FAST BACTERIA |
 | | Mycobacterium |  | | Gram stain: | - (acid - fast) | | Microscopic appearance: | rods; sometimes cocobacilli or filaments |
| Oxygen relationship: | aerobes | | Motility: | nonmotile | | Catalase test: | positive | | Oxidase test: | negative | | Spores: | non-spore forming |
|
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the causative agent of Tuberculosis |
| Mycobacterium leprae is the causative agent of Leprosy |
 |
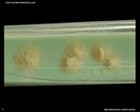 Mycobacterium tuberculosis
on L÷wenstein-Jensen medium |
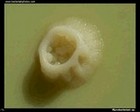 Mycobacterium sp.
on Ogawa medium |
 Mycobacterium fortuitum
on blood agar |
 Mycobacterium vaccae |
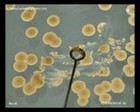 Mycobacterium sp. |
 Mycobacterium sp.
on M2 agar |
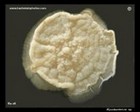 Mycobacterium sp.
colony on M2 agar |
 Mycobacterium sp.
and
Staphylococcus aureus
Ziehl-Neelsen stain |
OTHER BACTERIA |
 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
on Mueller-Hinton agar |

Chryseobacterium indologenes
on Mueller-Hinton agar |
 Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
on Columbia horse blood agar |
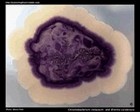 Chromobacterium violaceum and
Erwinia carotovora |
 |
 Pasteurella multocida
on blood agar |
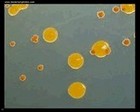 Chryseobacterium indologenes
and an actinomycete
on Mueller-Hinton agar |

Micrococcus luteus
on tryptic soy agar |
 Aeromonas hydrophila
on CLED agar |
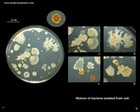 Mixture of bacteria
on agar plate |
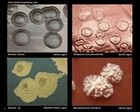 Bacterial colonies |

Bacteria and pigment production |
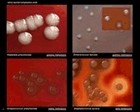 Bacterial colonies and hemolysis |
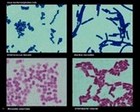 Bacteria: Light microscopy |
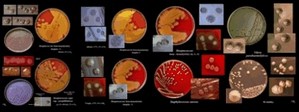 BACTERIA |
 Bacteria images |
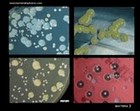 Colonies of various bacteria |
 Bacteria photos |
|
| | | |
DISK DIFFUSION METHOD
FOR TESTING OF ANTIBIOTIC SUSCEPTIBILITY OF BACTERIA | |
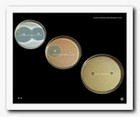 Susceptibility testing of bacteria |
 The disc diffusion test |
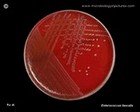
 The disc diffusion test
(Serratia marcescens):
antibiotic resistance |
 The disc diffusion method |
| |
| |
|