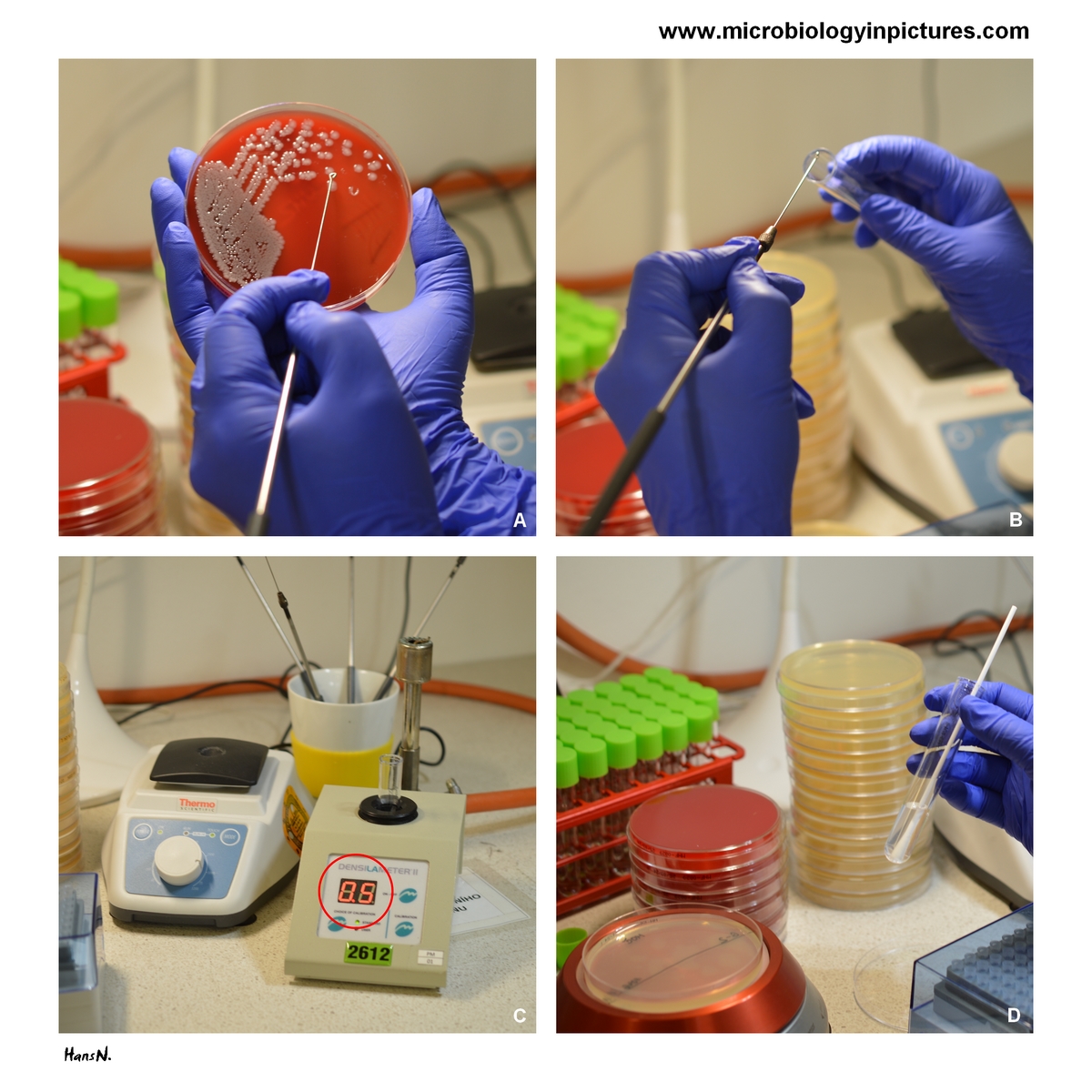
A Picking Colonies from an Agar Plate
Begin by identifying one or more morphologically similar colonies on an agar plate. Use a sterile inoculation loop to carefully pick a small portion of the colony. This ensures that the sample represents a pure culture, minimizing the risk of contamination that could affect the test results.
B Suspending the Colony in Saline Solution
Transfer the collected bacteria into a tube containing sterile saline solution. Vortex or mix the suspension thoroughly to ensure the bacteria are evenly distributed. Homogenization is essential for accurate turbidity measurement in the next step.
C Adjusting Turbidity to 0.5 McFarland Standard
Measure the turbidity of the bacterial suspension using a spectrophotometer or a turbidity meter. Adjust the concentration by either diluting with more saline or adding additional bacteria until the turbidity matches 0.5 McFarland. This standard corresponds to a bacterial density of approximately 1.5×10^8 colony-forming units (CFU) per milliliter, ensuring consistency across tests.
D Preparing the Sterile Cotton Swab
Dip a sterile cotton swab into the standardized bacterial suspension. Gently press the swab against the inner wall of the tube to remove excess fluid, leaving it saturated but not dripping. This ensures even distribution of bacteria on the agar surface.
Text generated with the help of OpenAI's language model, ChatGPT.
30.12.2024