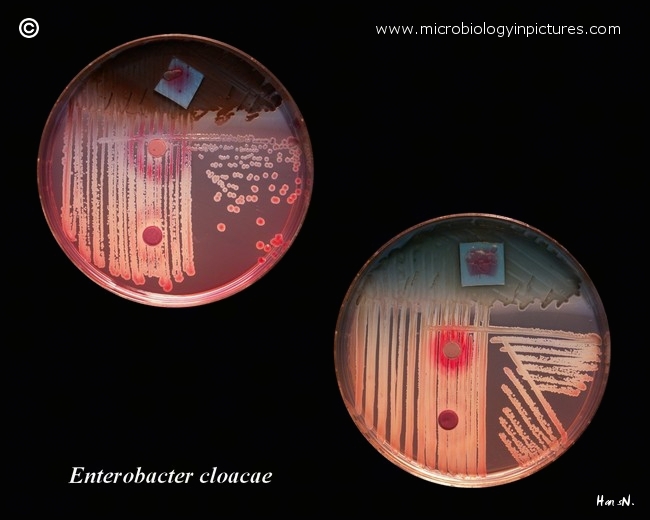
Enterobacter cloacae on Endo agar with biochemical slope. Cultivation 24 hours, 37°C.
Typical biochemical properties of E.cloacae:
- lactose fermentation (compare with lactose-positive colonies of E.coli on Endo)
- sucrose fermentation (red coloured agar and colonies around sucrose tablet)
- D-mannitol fermentation (red coloured agar and colonies around mannitol tablet; a weak reaction in both strains)
- acid from glucose with gas
- urea usually positive (bluish color of the biochemical slope)
- hydrogen sulfide negative (compare with Salmonella enterica)
- Indole production (negative)
- Voges-Proskauer test (positive)
- Simmons citrate (positive)
- Gelatin hydrolysis (negative; unlike Serratia marcescens)
- Esculin hydrolysis (negative; unlike Klebsiella pneumoniae)
- Lysin decarboxylase (typically negative)
- Arginine dihydrolase (typically positive)
- Ornithine decarboxylase (typically positive)
Other (more or less) necessary tests for identification are:
Comparison of basic test results for E.coli, K.pneumonia, E.cloacae and S.marcescens you can find here.