Streptococcus pneumoniae
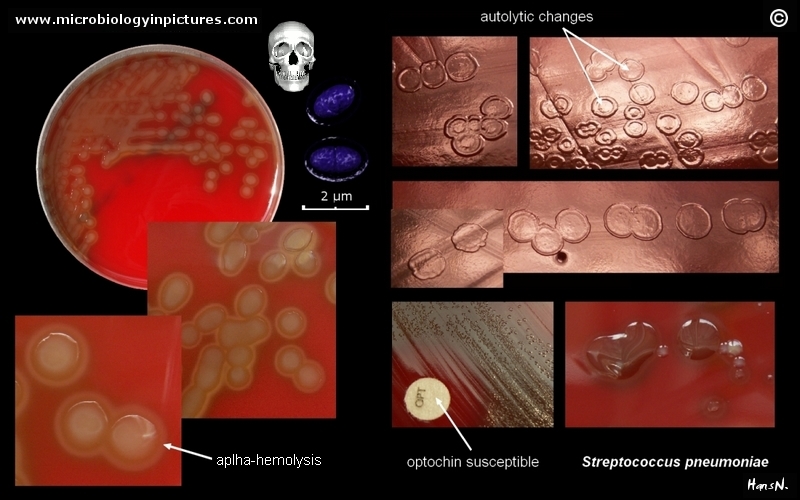
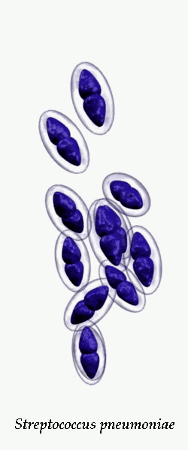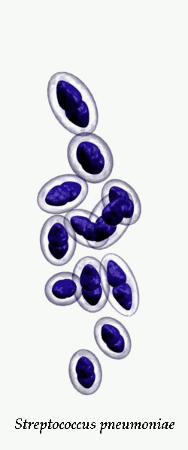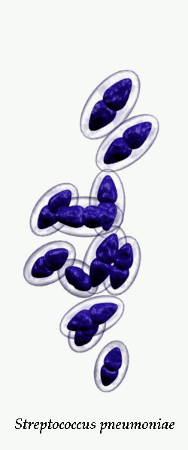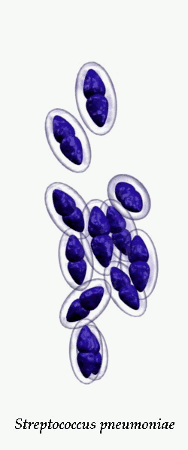
Streptococcus pneumoniae in clinical material occurs in two distinctive forms. Encapsulated, virulent strains isolated e.g., from sputum in
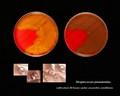
patients with acute pneumonia, often forming highly mucoid, glistening colonies (production of capsular polysaccharide) surrounded by a zone of alpha-hemolysis. After prolonged cultivation (48 hours in
an aerobic atmosphere enriched with 5-10% carbon dioxide) they are often able to form colonies about 5 mm in diameter.
In throat swabs Streptococcus pneumoniae can occur in its avirulent form (oropharyngeal carriage of pneumococci is common and they are considered to be part of normal flora). The colonies are only 0.5-2 mm in diameter,
surrounded by zone of alpha-hemolysis and due to autolysis, often develop a dimpled rather a craterlike appearance. These colonies are someties morphologically indistinguishable
from those of viridans streptococci but unlike viridas streptococci are sensitive to optochin and soluble in sodium desoxycholate (bile salts).
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a significant human pathogenic bacterium. S.pneumoniae was recognized as a major cause of pneumonia in the late 19th century and is the subject of many humoral immunity studies. Despite the name, the organism causes many types of pneumococcal infection other than pneumonia, including acute sinusitis, otitis media, meningitis, bacteremia, sepsis, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, endocarditis, peritonitis, pericarditis, cellulitis, and brain abscess. S.pneumoniae is the most common cause of bacterial meningitis in adults and children, and is one of the top two isolates found in ear infection, otitis media. Pneumococcal pneumonia is more common in the very young and the very old. S.pneumoniae can be differentiated from viridans streptococci, some of which are also alpha hemolytic, using an optochin test, as S.pneumoniae is optochin sensitive. S.pneumoniae can also be distinguished based on its sensitivity to lysis by bile. The encapsulated, gram-positive coccoid bacteria have a distinctive morphology on gram stain, the so-called, "lancet shape". It has a polysaccharide capsule that acts as a virulence factor for the organism; more than 90 different serotypes are known, and these types differ in virulence.
Streptococcus pneumoniae basic characteristics
- GRAM-POSITIVE COCCI
- NONMOTILE
- NON-SPORE-FORMING
- CATALASE: NEGATIVE
- OXIDASE: NEGATIVE
- FACULTATIVELY ANAEROBIC
Identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae
- The optochin test (sensitive to optochin)
- The bile solubility test (positive)
- Capsular swelling reaction
Antibiotic treatment of Streptococcus pneumoniae infections
IF SUSCEPTIBLE:
- penicillin
- ampicillin
- amoxicillin
- cephalosporins I, II
- macrolides
PENICILLIN RESISTANT:
- cephalosporins III (e.g., cefotaxime, ceftriaxone)
ALTERNATIVES:
- vancomycin
- chloramphenicol
- List of antibiotics (Wikipedia)
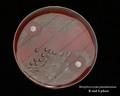
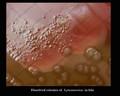
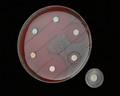
Streptococcus pneumoniae colonies on blood agar
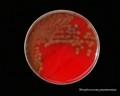
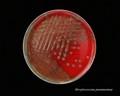
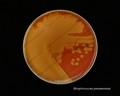

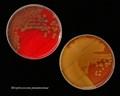
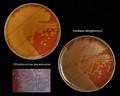
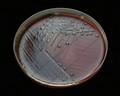

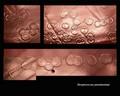
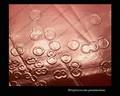
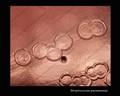
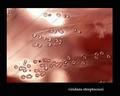


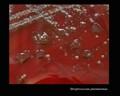


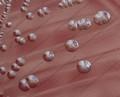
Streptococcus pneumoniae alpha-hemolysis



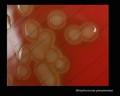
Streptococcus pneumoniae; the optochin test
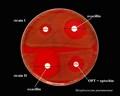
Streptococcus pneumoniae; the bile solubility test

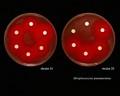
Streptococcus pneumoniae susceptibility testing
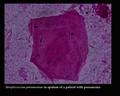
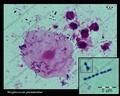
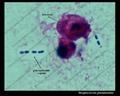
Streptococcus pneumoniae Gram stain
Useful Links
WIKIPEDIACENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION (CDC)
- Identification and Characterization of Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PCR for Detection and Characterization of Bacterial Meningitis Pathogens
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
E-MEDICINE