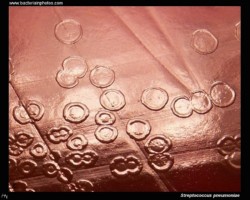
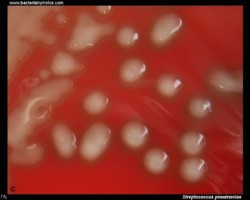
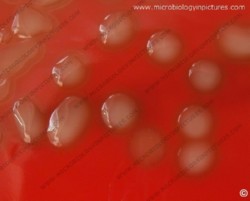
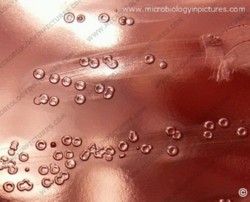
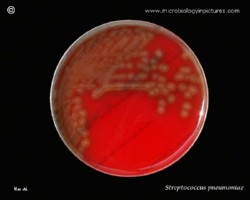
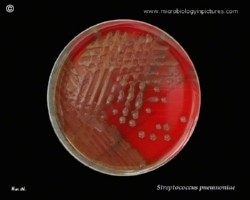
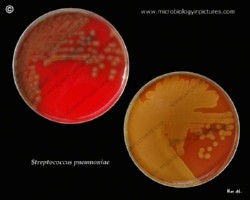
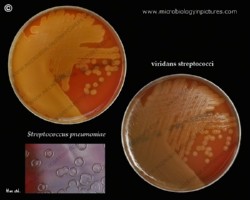
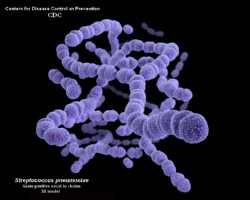
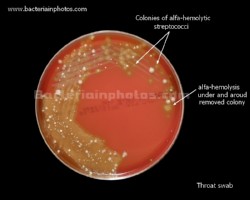
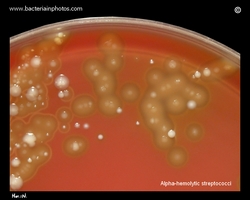
On blood agar plates they form colonies ranging from pinpoint size to 2-3 mm in diameter after 24 hours. A distinctive feature of streptococcal growth on blood agar is the production by many species of alpha- or beta-hemolysis. In the alpha-hemolytic reaction, erythrocytes are not completely lysed but growth is surrounded by greenish discoloration of the agar.
VIRIDANS STREPTOCOCCI
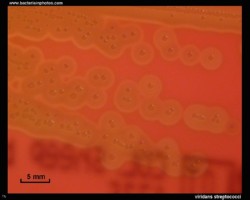
Viridans streptococci are alpha-hemolytic or nonhemolytic and lack both the group carbohydrate antigen of the pyogenic streptococci and the capsular antigens of the pneumococcus.
Importance: viridans streptococci are normal inhabitants of the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and female genital tract. Some of them can be the causative agents of subacute endocarditis, abscesses and infections in neutropenic patients.
- Mitis Group: e.g., S.mitis, S.oralis, S.sanguis (part of the normal dental plaque flora)
- Anginosus Group: e.g., S.anginosus, S.constellatus, S.intermedius (oral, genitourinary flora, gastrointestinal tract); can be beta-hemolytic
- Mutans Group: e.g., S.mutans (associated with dental caries); some strains can be beta-hemolytic
- Salivarius Group: e.g., S.salivarius, S.vestibularis (oral cavity)
- Bovis Group: e.g., S.bovis
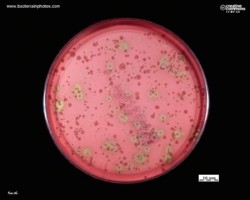
Examples of viridans streptococci
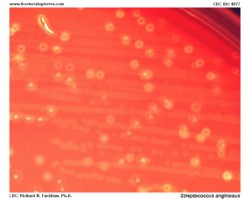
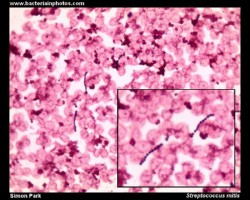
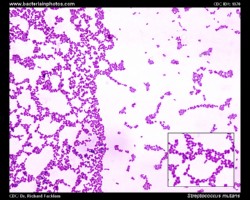
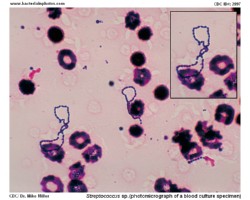
Treatment of endocarditis caused by viridans streptococci
- penicillin G
(+ gentamicin for synergy) - ceftriaxone
- vancomycin
- tetracyclines
- macrolides
- lincosamides
Alternatives:
PNEUMOCOCCUS (Streptococcus pneumoniae)
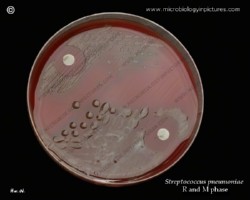
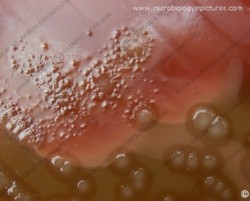
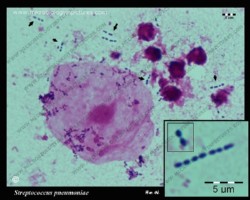
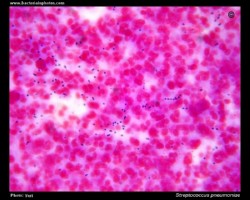
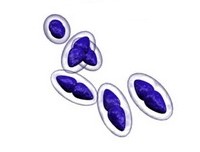
The pneumococcus is a Gram-positive bacterium, frequently of lancet shape, usually arranged in pairs or short chains. The virulent forms possess an easily demonstrable capsule. Alpha-hemolytic colonies with depressions in their centers are characteristic of pneumococci. Colonies of viridans streptococci usually have a domed appearance. On blood agar, encapsulated pneumococci produce round, glistening colonies surrounded by a zone of alpha-hemolysis.Importance: Streptococcus pneumoniae is a major cause of both acute bacterial pneumonia and acute purulent meningitis. Other pneumococcal infections include otitis media, sinusitis, and endocarditis.
- Oropharyngeal carriage of pneumococci is common
- An important agent of community-acquired pneumonia
- Otitis media, sinusitis, meningitis, endocarditis
- Require elevated CO2 concentrations (incubation in an atmosphere containing 5% - 10% CO2)
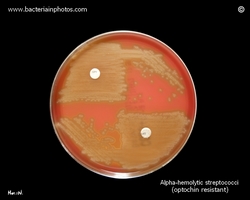
- Sensitive to optochin
- Soluble in bile salts
- Positive Quellung test